Python can really feel intimidating in case you’re not a developer. You see scripts flying round Twitter, hear folks speaking about automation and APIs, and surprise if it’s value studying—and even potential—with out a pc science diploma.
However right here’s the reality: Search engine marketing is stuffed with repetitive, time-consuming duties that Python can automate in minutes. Issues like checking for damaged hyperlinks, scraping metadata, analyzing rankings, and auditing on-page Search engine marketing are all doable with a couple of traces of code. And due to instruments like ChatGPT and Google Colab, it’s by no means been simpler to get began.
On this information, I’ll present you methods to begin studying.
Search engine marketing is filled with repetitive, guide work. Python helps you automate repetitive duties, extract insights from large datasets (like tens of hundreds of key phrases or URLs), and construct technical expertise that assist you deal with just about any Search engine marketing downside: debugging JavaScript points, parsing complicated sitemaps, or utilizing APIs.
Past that, studying Python helps you:
Perceive how web sites and net information work (consider it or not, the web is just not tubes).Collaborate with builders extra successfully (how else are you planning to generate hundreds of location-specific pages for that programmatic Search engine marketing marketing campaign?)Study programming logic that interprets to different languages and instruments, like constructing Google Apps Scripts to automate reporting in Google Sheets, or writing Liquid templates for dynamic web page creation in headless CMSs.
And in 2025, you’re not studying Python alone. LLMs can clarify error messages. Google Colab permits you to run notebooks with out setup. It’s by no means been simpler.
LLMs can deal with most error messages with ease—irrespective of how dumb they might be.
You don’t should be an professional or set up a fancy native setup. You simply want a browser, some curiosity, and a willingness to interrupt issues.
I like to recommend beginning with a hands-on, beginner-friendly course. I used Replit’s 100 Days of Python and extremely suggest it.
Right here’s what you’ll want to know:
1. Instruments to write down and run Python
Earlier than you’ll be able to write any Python code, you want a spot to do it — that’s what we name an “atmosphere.” Consider it like a workspace the place you’ll be able to kind, check, and run your scripts.
Selecting the best atmosphere is necessary as a result of it impacts how simply you will get began and whether or not you run into technical points that decelerate your studying.
Listed below are three nice choices relying in your preferences and expertise degree:
Replit: A browser-based IDE (Built-in Growth Surroundings), which suggests it provides you a spot to write down, run, and debug your Python code — all out of your net browser. You don’t want to put in something — simply join, open a brand new venture, and begin coding. It even contains AI options that can assist you write and debug Python scripts in actual time. Go to Replit.Google Colab: A free instrument from Google that permits you to run Python notebooks within the cloud. It’s nice for Search engine marketing duties involving information evaluation, scraping, or machine studying. It’s also possible to share notebooks like Google Docs, which is ideal for collaboration. Go to Google Colab.VS Code + Python interpreter: Should you choose to work domestically or need extra management over your setup, set up Visible Studio Code and the Python extension. This provides you full flexibility, entry to your file system, and help for superior workflows like Git versioning or utilizing digital environments. Go to the VS Code web site.
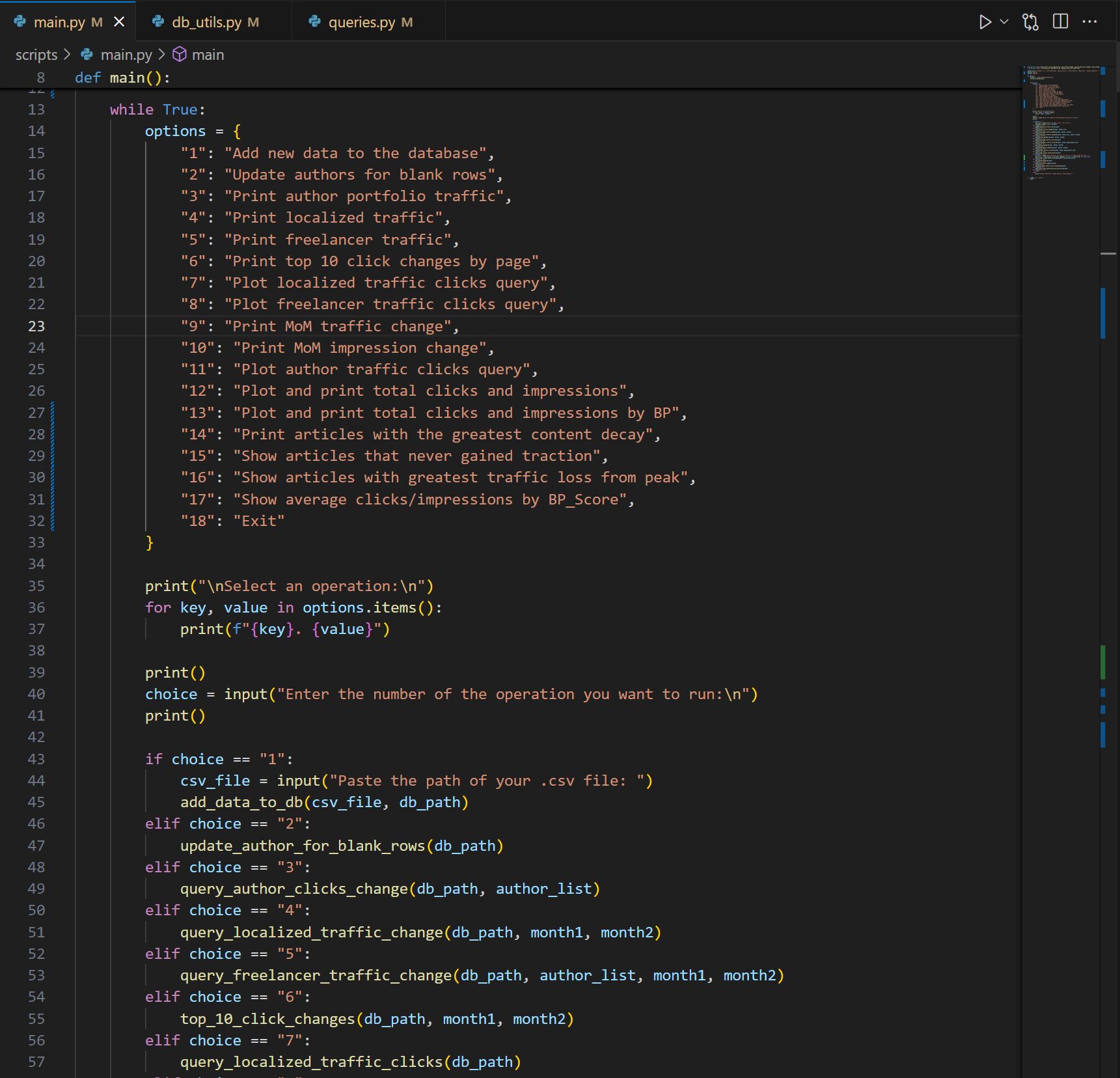

My weblog reporting program, in-built heavy conjunction with ChatGPT.
You don’t want to start out right here—however long-term, getting snug with native growth gives you extra energy and adaptability as your initiatives develop extra complicated.
Should you’re uncertain the place to start out, go along with Replit or Colab. They get rid of setup friction so you’ll be able to deal with studying and experimenting with Search engine marketing scripts proper away.
2. Key ideas to study early
You don’t have to grasp Python to start out utilizing it for Search engine marketing, however you need to perceive a couple of foundational ideas. These are the constructing blocks of almost each Python script you’ll write.
Variables, loops, and capabilities: Variables retailer information like a listing of URLs. Loops allow you to repeat an motion (like checking HTTP standing codes for each web page). Capabilities allow you to bundle actions into reusable blocks. These three concepts will energy 90% of your automation. You’ll be able to study extra about these ideas by newbie tutorials like Python for Newcomers – Study Python Programming or W3Schools Python Tutorial.Lists, dictionaries, and conditionals: Lists assist you work with collections (like all of your website’s pages). Dictionaries retailer information in pairs (like URL + title). Conditionals (like if, else) assist you resolve what to do relying on what the script finds. These are particularly helpful for branching logic or filtering outcomes. You’ll be able to discover these subjects additional with the W3Schools Python Information Buildings information and LearnPython.org’s management move tutorial.Importing and utilizing libraries: Python has hundreds of libraries: pre-written packages that do heavy lifting for you. For instance, requests permits you to ship HTTP requests, beautifulsoup4 parses HTML, and pandas handles spreadsheets and information evaluation. You’ll use these in virtually each Search engine marketing job. Take a look at The Python Requests Module by Actual Python, Stunning Soup: Internet Scraping with Python for parsing HTML, and Python Pandas Tutorial from DataCamp for working with information in Search engine marketing audits.

These are my precise notes from working by Replit’s 100 Days of Python course.
These ideas might sound summary now, however they arrive to life when you begin utilizing them. And the excellent news? Most Search engine marketing scripts reuse the identical patterns repeatedly. Study these fundamentals as soon as and you may apply them in every single place.
3. Core Search engine marketing-related Python expertise
These are the bread-and-butter expertise you’ll use in almost each Search engine marketing script. They’re not complicated individually, however when mixed, they allow you to audit websites, scrape information, construct reviews, and automate repetitive work.
Making HTTP requests: That is how Python masses a webpage behind the scenes. Utilizing the requests library, you’ll be able to examine a web page’s standing code (like 200 or 404), fetch HTML content material, or simulate a crawl. Study extra from Actual Python’s information to the Requests module.Parsing HTML: After fetching a web page, you’ll usually wish to extract particular components, just like the title tag, meta description, or all picture alt attributes. That’s the place beautifulsoup4 is available in. It helps you navigate and search HTML like a professional. This Actual Python tutorial explains precisely the way it works.Studying and writing CSVs: Search engine marketing information lives in spreadsheets: rankings, URLs, metadata, and so on. Python can learn and write CSVs utilizing the built-in csv module or the extra highly effective pandas library. Learn the way with this pandas tutorial from DataCamp.Utilizing APIs: Many Search engine marketing instruments (like Ahrefs, Google Search Console, or Screaming Frog) provide APIs — interfaces that allow you to fetch information in structured codecs like JSON. With Python’s requests and json libraries, you’ll be able to pull that information into your individual reviews or dashboards. Right here’s a primary overview of APIs with Python.

The Pandas library is unbelievably helpful for information evaluation, reporting, cleansing information, and 100 different issues.
As soon as you realize these 4 expertise, you’ll be able to construct instruments that crawl, extract, clear, and analyze Search engine marketing information. Fairly cool.
These initiatives are easy, sensible, and might be constructed with fewer than 20 traces of code.
1. Test if pages are utilizing HTTPS
One of many easiest but most helpful checks you’ll be able to automate with Python is verifying whether or not a set of URLs is utilizing HTTPS. Should you’re auditing a shopper’s website or reviewing competitor URLs, it helps to know which pages are nonetheless utilizing insecure HTTP.
This script reads a listing of URLs from a CSV file, makes an HTTP request to every one, and prints the standing code. A standing code of 200 means the web page is accessible. If the request fails (e.g., the positioning is down or the protocol is incorrect), it can inform you that too.
import csv
import requests
with open(‘urls.csv’, ‘r’) as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
for row in reader:
url = row[0]
attempt:
r = requests.get(url)
print(f”{url}: {r.status_code}”)
besides:
print(f”{url}: Failed to attach”)
2. Test for lacking picture alt attributes
Lacking alt textual content is a typical on-page problem, particularly on older pages or giant websites. Slightly than checking each web page manually, you should utilize Python to scan any web page and flag photographs lacking an alt attribute. This script fetches the web page HTML, identifies all <img> tags, and prints out the src of any picture lacking descriptive alt textual content.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url=”
r = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.textual content, ‘html.parser’)
photographs = soup.find_all(‘img’)
for img in photographs:
if not img.get(‘alt’):
print(img.get(‘src’))
3. Scrape title and meta description tags
With this script, you’ll be able to enter a listing of URLs, extract every web page’s <title> and <meta title=“description”> content material, and save the outcomes to a CSV file. This makes it simple to identify lacking, duplicated, or poorly written metadata at scale — and take motion quick.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
urls = [‘ ‘
with open(‘meta_data.csv’, ‘w’, newline=””) as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow([‘URL’, ‘Title’, ‘Meta Description’])
for url in urls:
r = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.textual content, ‘html.parser’)
title = soup.title.string if soup.title else ‘No title’
desc_tag = soup.discover(‘meta’, attrs={‘title’: ‘description’})
desc = desc_tag[‘content’] if desc_tag else ‘No description’
author.writerow([url, title, desc])
4. Utilizing Python with the Ahrefs API
Should you’re an Ahrefs buyer with API entry, you should utilize Python to faucet straight into our information, fetching backlinks, key phrases, rankings, and extra. This opens the door to large-scale Search engine marketing workflows: auditing hundreds of pages, analyzing competitor hyperlink profiles, or automating content material reporting.
For instance, you may:
Monitor new backlinks to your website every day and log them to a Google SheetAutomatically pull your prime natural pages each month for content material reportingTrack key phrase rankings throughout a number of websites and spot developments quicker than utilizing the UI alone
Right here’s a easy instance to fetch backlink information:
import requests
url = ”
r = requests.get(url)
information = r.json()
print(information)
You’ll want an Ahrefs API subscription and entry token to run these scripts. Full documentation and endpoint particulars can be found within the Ahrefs API docs.
Patrick Stox, aka Mr Technical Search engine marketing, is all the time tinkering with Python, and he’s made tons of free instruments and scripts freely out there in Google Colab. Listed below are a couple of of my private favorites:
Redirect matching script: This script automates 1:1 redirect mapping by matching outdated and new URLs through full-text similarity. Add your before-and-after URLs, run the pocket book, and let it counsel redirects for you. It’s extremely useful throughout migrations. Run the script right here.Web page title similarity report: Google usually rewrites web page titles in search outcomes. This instrument compares your submitted titles (through Ahrefs information) with what Google truly shows, utilizing a BERT mannequin to measure semantic similarity. Ideally suited for large-scale title audits. Run the script right here.Visitors forecasting script: Featured in our Search engine marketing Forecasting information, this script makes use of historic site visitors information to foretell future efficiency. Nice for setting expectations with purchasers or making the case for continued funding. Run the script right here.
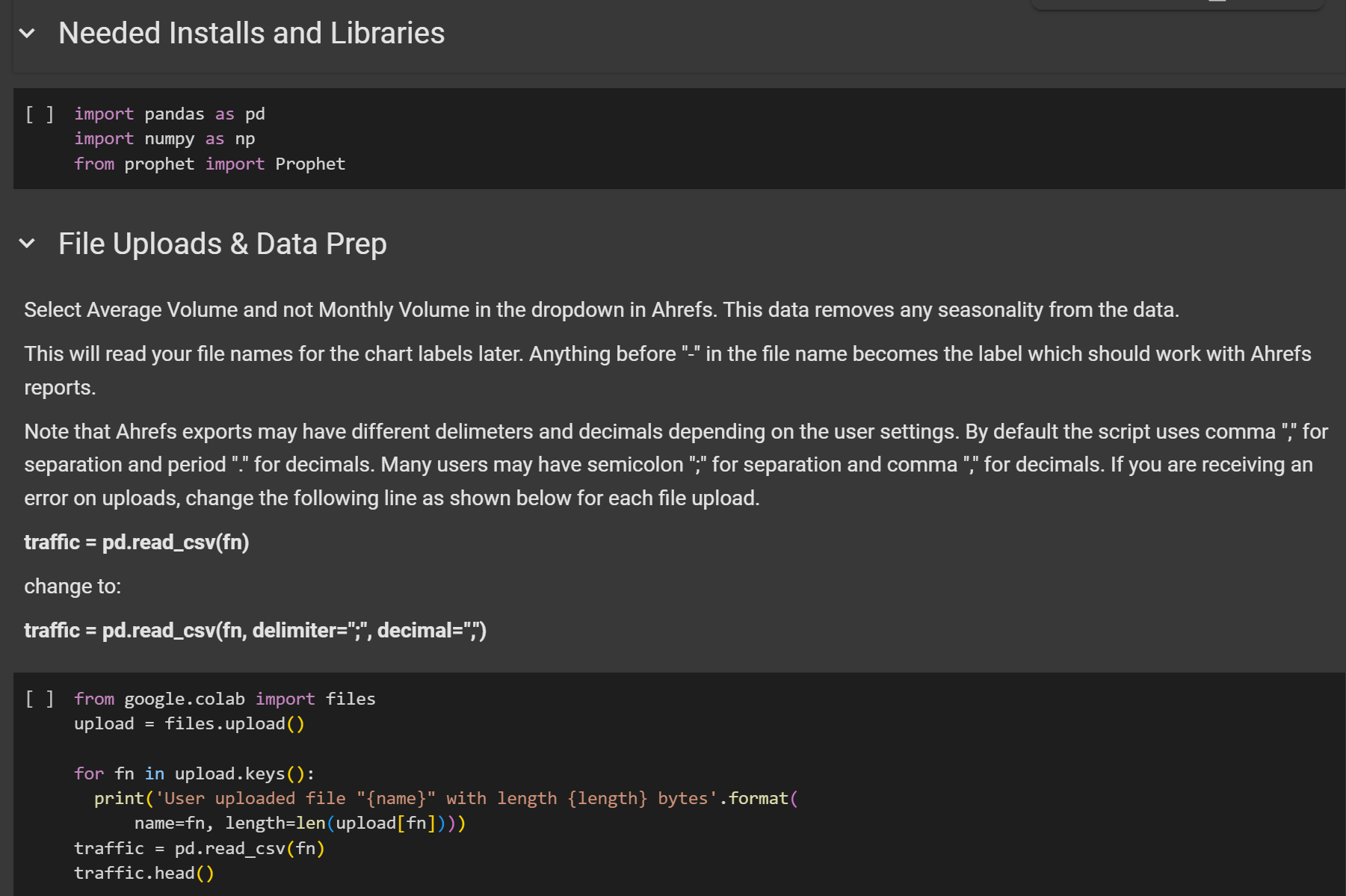

One in all Patrick’s scripts in Colab.
Study extra about this forecasting script in Patrick’s information to Search engine marketing forecasting.
Ultimate ideas
Python is likely one of the most impactful expertise you’ll be able to study as an Search engine marketing. Even a couple of primary scripts can save hours of labor and uncover insights you’d miss in any other case.
Begin small. Run your first script. Fork certainly one of Patrick’s instruments. Or spend half-hour with Replit’s Python course. It received’t take lengthy earlier than you’re pondering: why didn’t I do that sooner?
Bought questions? Ping me on Twitter.